Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases areClimate change refers to significant changes in global temperature, precipitation, wind patterns and other measures of climate that occur over several decades or longer Discover an AZ glossary of concise scientific explanations to help readers better understand climate change from science› en español Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respond

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
Greenhouse gas definition atmospheric science
Greenhouse gas definition atmospheric science-The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist




Global Warming Potential Definition And Examples
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time What are greenhouse gases?Noun phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape greenhouse gas Noun gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by
Define greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, The trapping of the sun's radiation in the Earth's atmosphere due to the presence of greenhouse gases The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities suchGreenhouse gases occur naturally and allow us to survive on Earth by warming air near Earth's surface Human activities are now increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which leads to changes in climate These changes are
Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space Greenhouse gases from dead trees play an important role in the overall environmental impact of ghost forests, a new study suggestsGreenhouse gases Sources As greenhouse gases are essential for the existence of life, they are present in the atmosphere in a trace amount Natural sources of GHGs are volcanos, respiration by living organisms, decay and combustion of organic matter, etc The amounts of GHGs are balanced in the atmosphere naturally by many physical, chemical




Runaway Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Global Warming Potential Definition And Examples
Greenhouse Gases The atmospheric concentrations of the major longlived greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), and carbon tetrachloride (CCI4) continue to increase because of human activities While the growth rates of most of these gases have What are "greenhouse gases?" The transparent windows of a greenhouse (or a car parked in the sunlight) transmit the warming visible rays of the sun, prevent the resulting warm air from leaving, and hence maintain a warmer environment inside than outside the structureThe heattrapping nature of carbon dioxide and other gases was demonstrated in the mid19th century 2 Their ability to affect the transfer of infrared energy through the atmosphere is the scientific basis of many instruments flown by NASA There is no question that increased levels of greenhouse gases must cause Earth to warm in response




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
With over one hundred thousand videos with full EnglishChinese subtitles, a builtin dictionary, pronunciation challenges and more, it's no wonder that there are 4 million users that are learning English on VoiceTube the fun wayFgases are often used as substitutes for ozonedepleting substances, because they do not damage the atmospheric ozone layer However, Fgases are powerful greenhouse gases, with a global warming effect up to 23 000 times greater than carbon dioxide (CO 2), and their emissions are rising strongly The emissions of Fgases in the EU almost doubled from 1990 to 14 – inAP Environmental Science Greenhouse Gases Study concepts, example questions & explanations for AP Environmental Science CREATE AN ACCOUNT Create Tests & Flashcards Home Embed All AP Environmental Science Resources 1 Diagnostic Test 149 Practice Tests Question of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept Example




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube
Definition Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface, the atmosphere and clouds This property causes the greenhouse effect Global warming from the increase in greenhouse gases has become a major scientific and political issue during the past decade That infrared radiation is trapped by greenhouse gases and particles in a planetary atmosphere and that the atmospheric CO2 level has increased by some 25 percent since 1850 because of fossil fuel combustion and land use (largely Greenhouse gases act like a blanket around Earth, trapping energy in the atmosphere and causing it to warm This phenomenon is called the greenhouse effect and is natural and necessary to support life on Earth However, the buildup of greenhouse gases can change Earth's climate and result in dangerous effects to human health and welfare and to




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
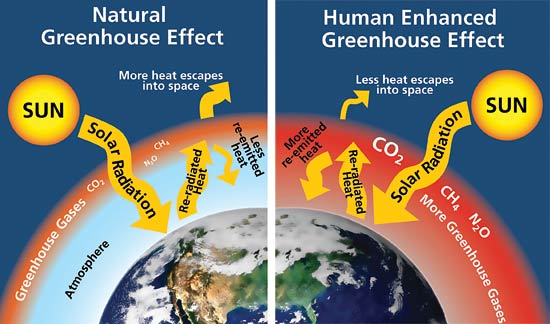
These humangenerated gases enhance the natural greenhouse effect and further warm the surface In addition to the direct effect, the warming that results from increased concentrations of longlived greenhouse gases can be amplified by other processes A key example is water vapour amplification (Box 13) Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effectDefine greenhouse gases greenhouse gases synonyms, greenhouse gases pronunciation, greenhouse gases translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide and lowlevel ozone
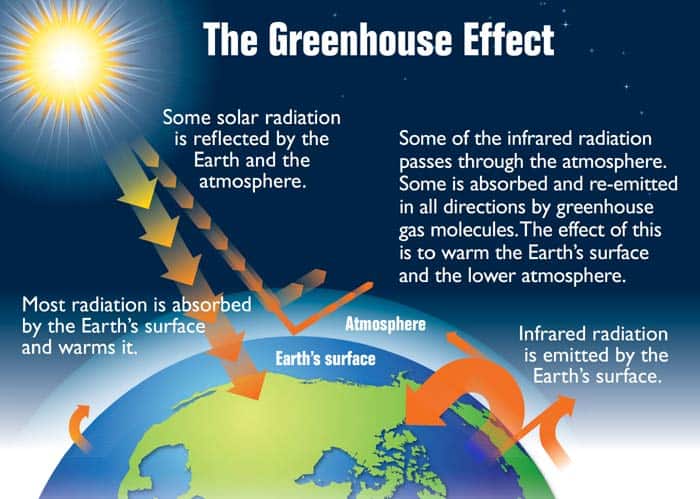



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change



Methane Emissions In The Oil And Gas Industry American Geosciences Institute
Greenhouse gases absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the Earth's surface release infrared radiation in all directions, which keeps the Earth warmMuch like the glass of a greenhouse, gases in Earth's atmosphere sustain life by trapping the sun's heat These "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know itGreenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time



1




Science Vincent
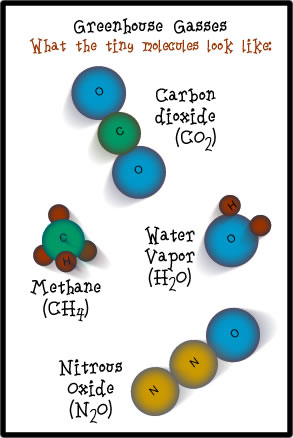
Greenhouse gases Global average concentrations of all the major longlived greenhouse gases continue to rise in the atmosphere, with the global annual mean carbon dioxide concentration reaching 410 ppm and CO 2 equivalent reaching 508 ppm in 19; greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases Regulated Greenhouse Gases in • Regulations in CA targeted towards the following six gases (or classes of gases) through "Global Warming Solutions Act" 1 Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) 2 Methane (CH 4) 3 Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) • First three (CO 2, CH 4 and N 2 O) also occur naturally in atmosphere, ie
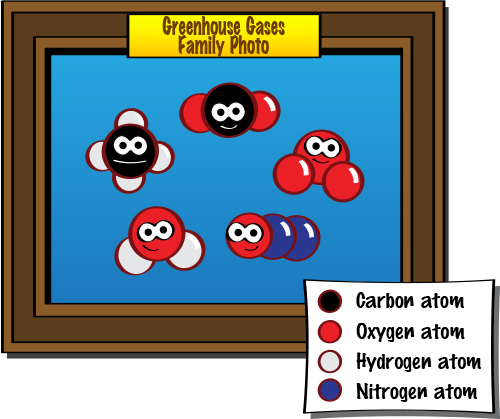



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
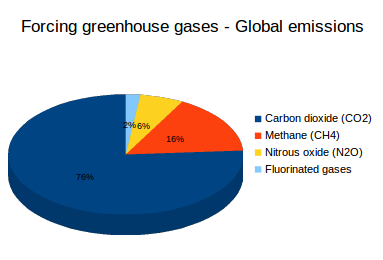
Suggested Citation"A Questions and Answers About Greenhouse Warming"Institute of Medicine, National Academy of Sciences, and National Academy of Engineering 1992 Policy Implications of Greenhouse Warming Mitigation, Adaptation, and the Science BaseGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming oneOverview of Greenhouse Gases Overview Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide Fluorinated Gases Total US Emissions in 19 = 6,558 Million Metric Tons of CO 2 equivalent (excludes land sector) Percentages may not add up to 100% due to independent rounding




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere By increasing the heat in theGreenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbonsGreenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth This process maintains the Earth's temperature at around 33 degrees Celsius warmer than it would otherwise be, allowing life on Earth to exist Enhanced



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
The rate of CO 2 accumulation in the atmosphere has increased with every passing decade since atmospheric measurements In 09, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established the socalled "Endangerment Finding" This defined a suite of six longlived greenhouse gases as "air pollution" Such air pollution was anticipated to represent a danger to the health and welfare of current and future generations Thus, the EPA has the authority to regulate these gases under the rules ofA greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gasesThis is called the "greenhouse effect"Most greenhouse gases are natural water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth Other greenhouse gases are carbon




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming
ACS Climate Science Toolkit Greenhouse Gases Temperature is a measure of the average energy of molecular motion in a sample of matter to and fro translation, intramolecular vibration (and lattice vibration in solids), and rotation (both entire molecules and intramolecular portions)Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6 Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau




What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Meaning And Several Examples




Are We All In Concordance With The Meaning Of The Word Conformance And Is Our Definition In Conformity With Standard Definitions Oldenburg 18 Greenhouse Gases Science And Technology Wiley Online Library




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Pin On Middle School Ngss Earth Science Resources
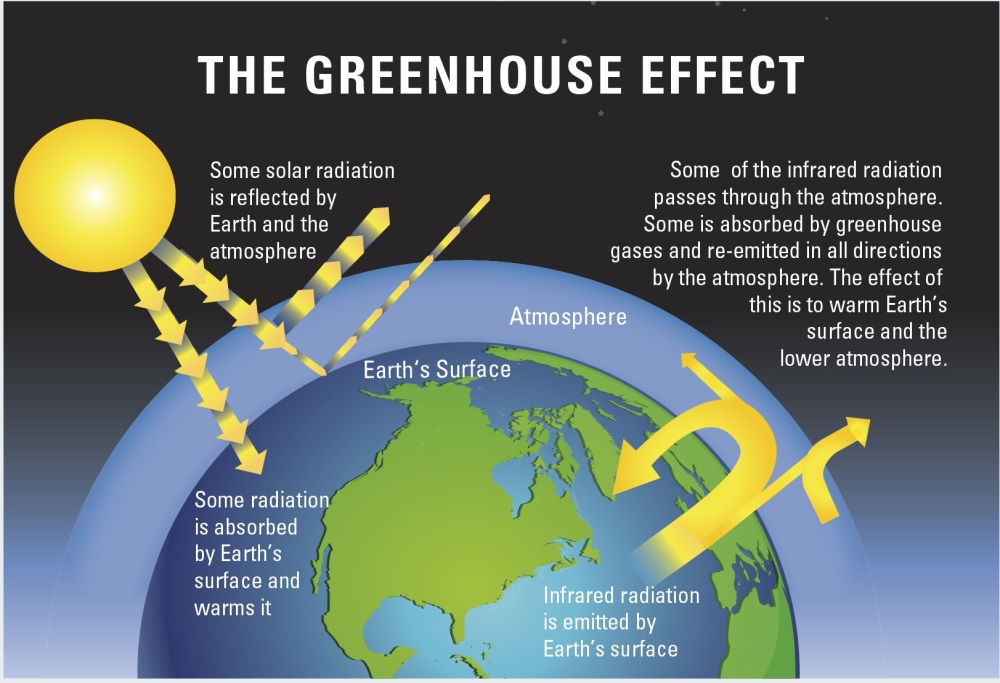



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




The Wall Street Journal Breaking News Business Financial Economic News World News And Video Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions
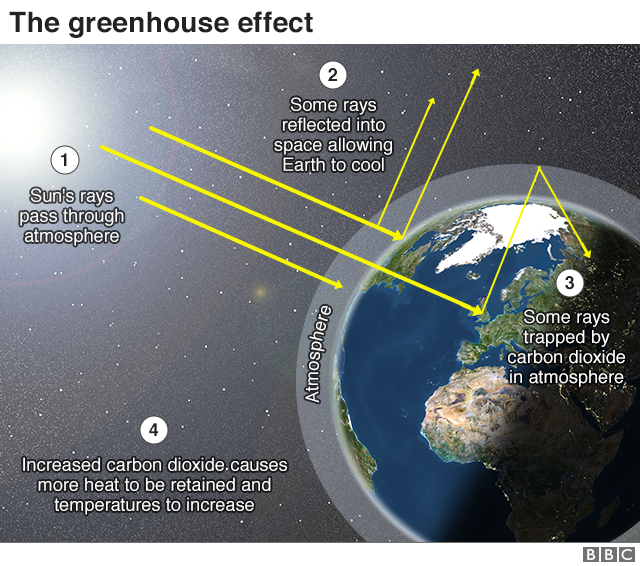



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News




What Are Greenhouse Gases Lesson For Kids Study Com




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming
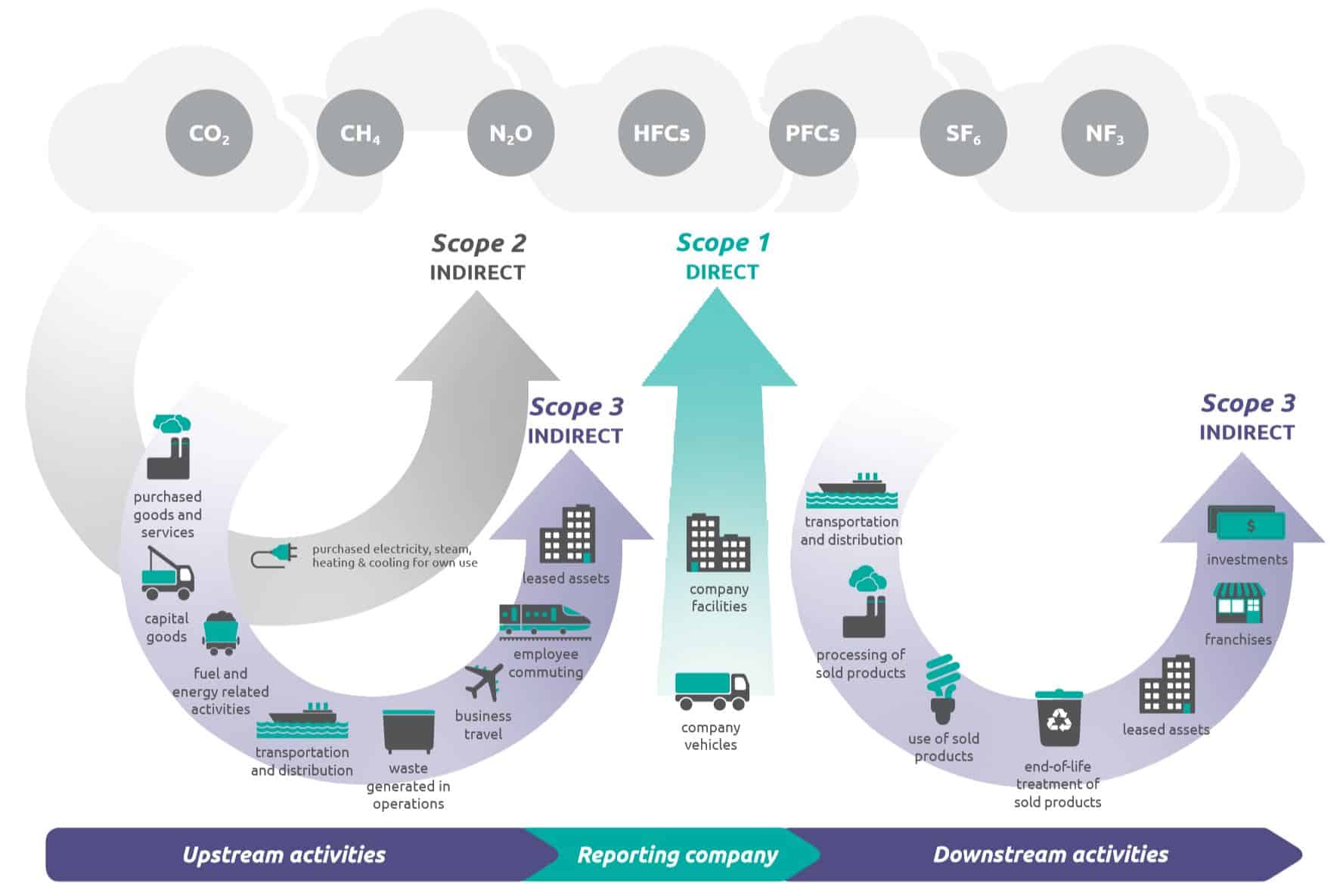



What Is The Difference Between Scope 1 2 And 3 Emissions Compare Your Footprint




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Uoe Sustainability We Re Starting With The Basics First Up Is A Definition Of Greenhouse Gases From The Scottishepa Help Make Climate Science Accessible To Others By Sharing These Posts




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
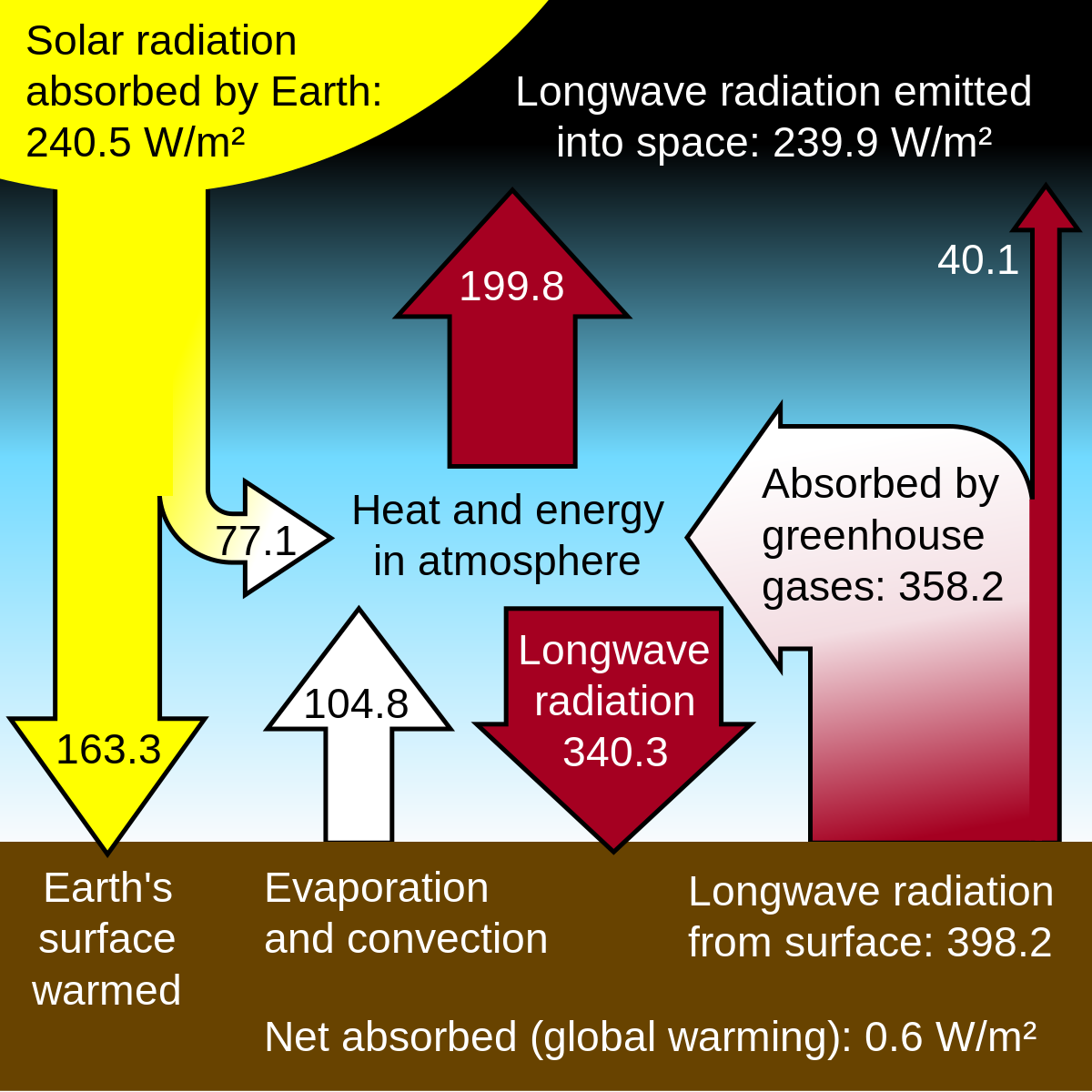



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
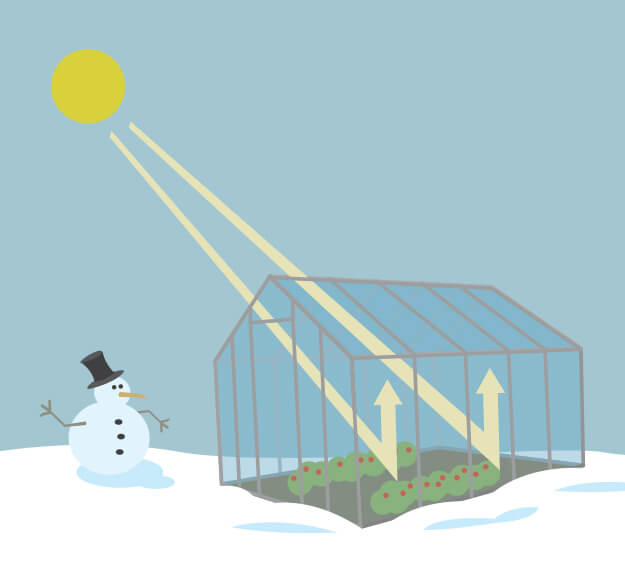




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
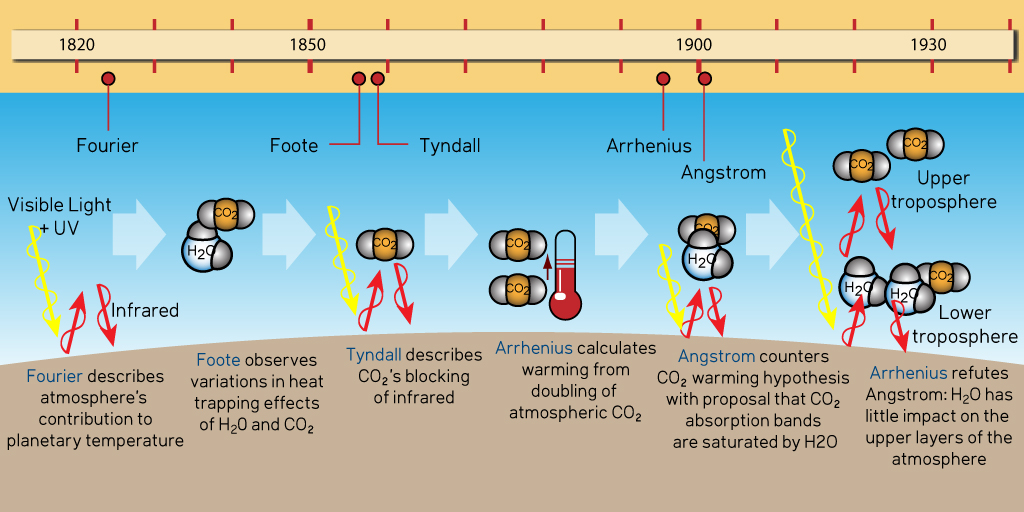



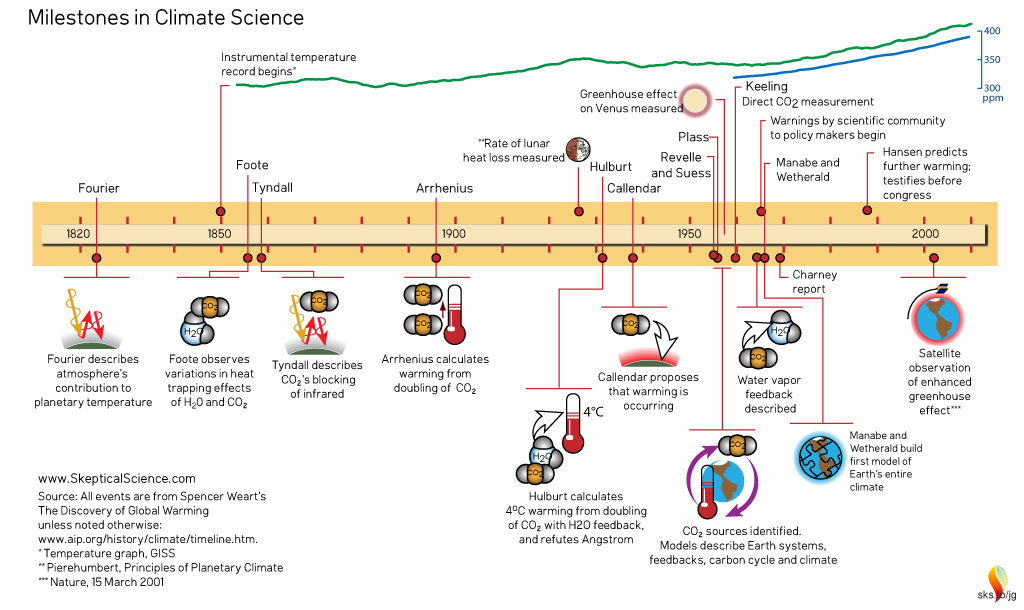
The History Of Climate Science



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids



Stc Umsl Edu Essj Unit4 13 Too cool for school Pdf




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
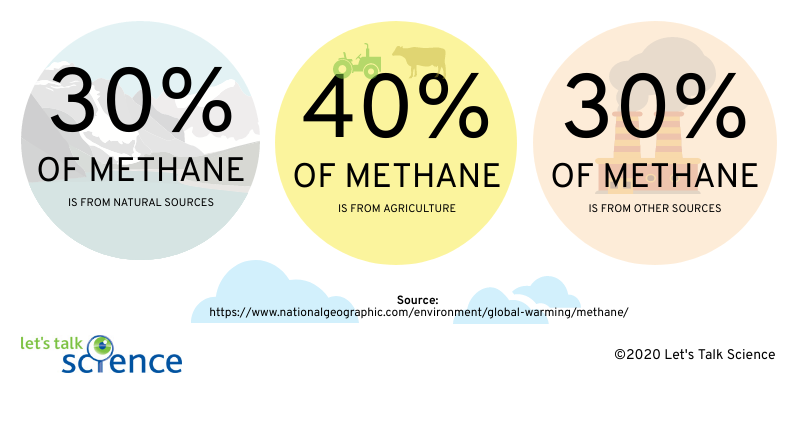



Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education




Practical Guide For The Definition Of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Targets In Line With Climate Science Science Based Targets




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Jargon Buster Science Based Targets




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com




Cap And Trade What Does It Mean For




Overall Idea Of The Lesson Instructional Objective



Environment For Kids Global Warming




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education



Greenhouse Effect




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Pick A Science Word And Write The Definition Chapter 15 Or Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube



The History Of Climate Science
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Science Doodle Note By Mrs Brosseau S Binder




Cap And Trade What Does It Mean For




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿